Disease Characterized By A Decrease In Alveolar Elasticity
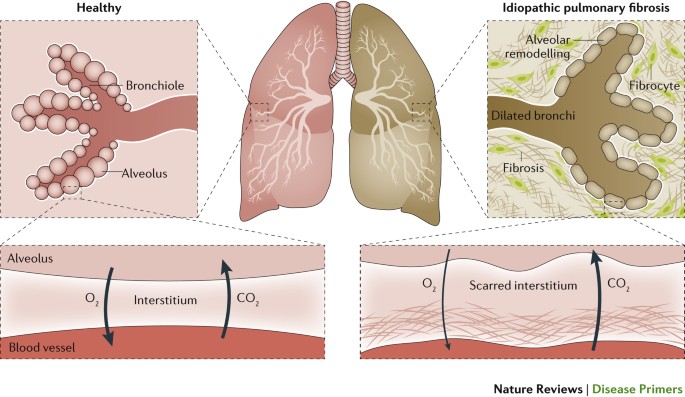
Disease characterized by a decrease in alveolar elasticity. Notably destructive event in alveolar bone has been linked to homocysteine Hcy metabolism however. Secrete pulmonary surfactant which ultimately decreases alveolar surface tension to prevent alveolar collapse as well as decreasing elastance and increasing compliance. This reduces the respiratory surface area and impairs gas exchange.
Heart aorta esophagus and bronchi. Positioning a patient so that gravity aids in the drainage of secretions form the bronchi and lobes of the lungs. The space in the chest between the lungs is called the.
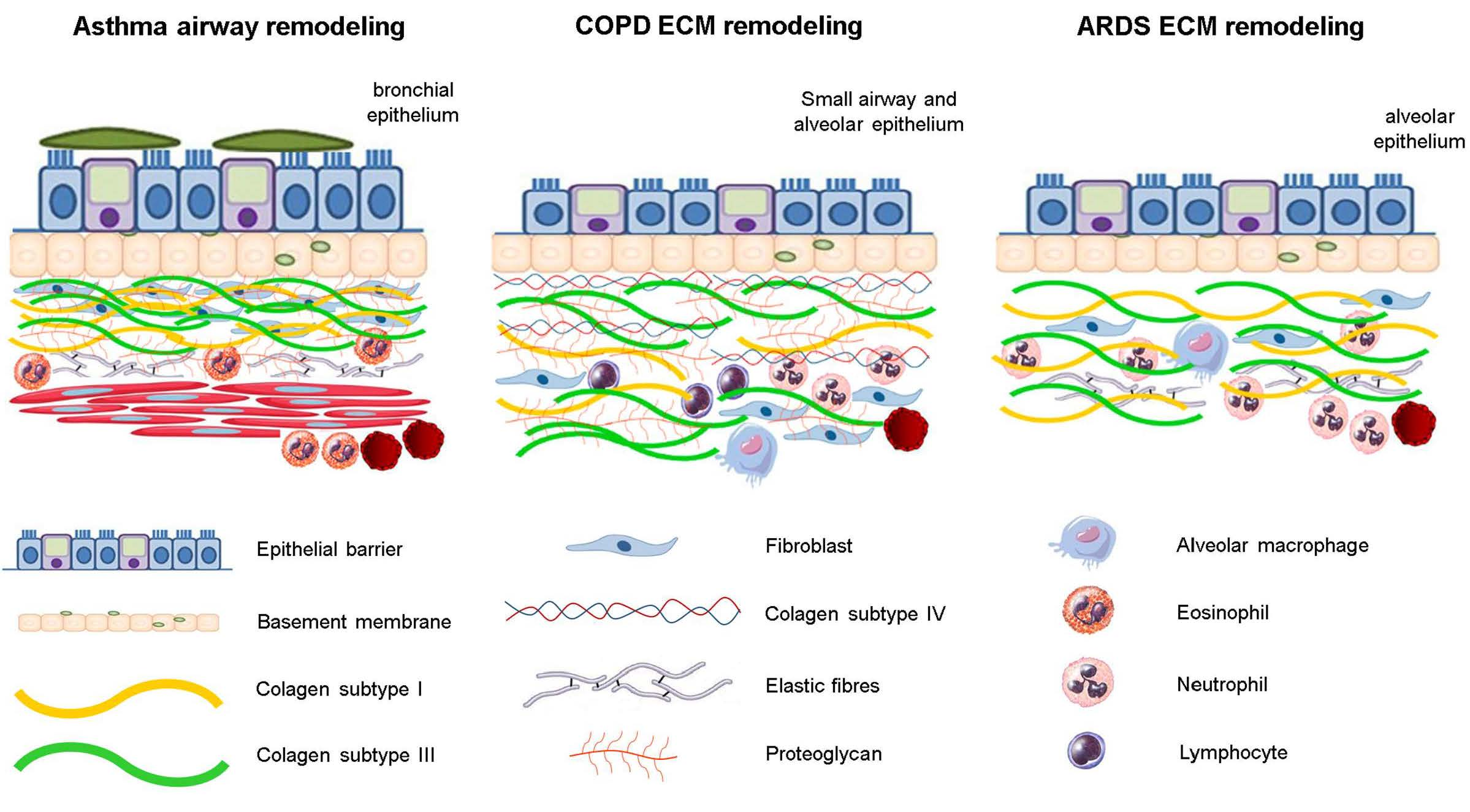
Caused by either smoking or an inherited deficiency of a protein called alpha 1-antitrypsin AAT. CH 16 Respiratory System. Irrigating or washing out of an organ with water or other fluid.
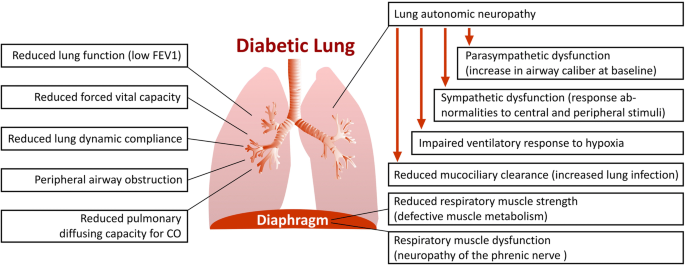
It has not been fully investigated. The mediastinum contains the. The exchange of oxygen O2 and carbon dioxide CO2.
Noninflammatory fluid that resembles serum but with less protein. This ability to proliferate makes type 2 pneumocytes helpful during lung damage. Irrigation of the antrum maxillary sinus in chronic or nonresponsive sinusitis.
A disease characterized by bronchial dilation that usually leads to secondary infection is. Disease characterized by a decrease in alveolar elasticity. It is a destructive disease described as a loss of lung elasticity and abnormal enlargement of the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles with destruction of the alveolar walls and capillary beds Porth 2005.
-- Less mA is needed to make a good exposure due to the increase of air trapped in the lungs. 1 Define emphysema A disease characterized by a decrease in alveolar elasticity.
Irrigating or washing out of an organ with water or other fluid.
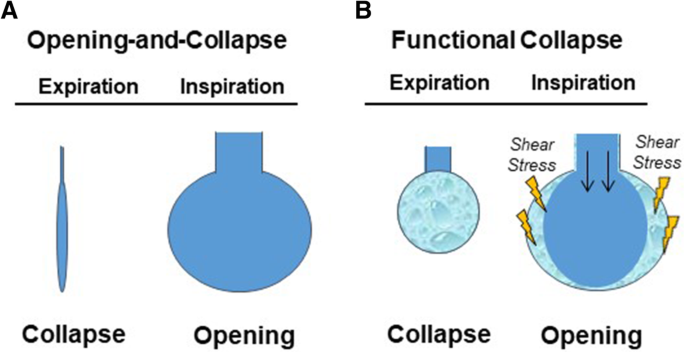
View Review Exam _1 Chapters 1-4 1docx from HEALTH 140 at Kauai Community College. The mediastinum contains the. CH 16 Respiratory System. Emphysema is a chronic respiratory disease where there is over-inflation of the air sacs alveoli in the lungs causing a decrease in lung function and often breathlessness. Type 2 Pneumocytes. This ability to proliferate makes type 2 pneumocytes helpful during lung damage. Periodontal disease results from poor oral hygiene and is characterized by a destructive process in periodontium that includes gingiva alveolar mucosa cementum periodontal ligament and alveolar bone. It is characterized by a rupture of the alveoli forming larger spaces in the lungs and excess mucus production which plugs terminal bronchioles trapping air in the alveoli. This reduces the respiratory surface area and impairs gas exchange.
It is a destructive disease described as a loss of lung elasticity and abnormal enlargement of the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles with destruction of the alveolar walls and capillary beds Porth 2005. It is a destructive disease described as a loss of lung elasticity and abnormal enlargement of the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles with destruction of the alveolar walls and capillary beds Porth 2005. View Review Exam _1 Chapters 1-4 1docx from HEALTH 140 at Kauai Community College. A disease characterized by bronchial dilation that usually leads to secondary infection is. Periodontal disease results from poor oral hygiene and is characterized by a destructive process in periodontium that includes gingiva alveolar mucosa cementum periodontal ligament and alveolar bone. Secrete pulmonary surfactant which ultimately decreases alveolar surface tension to prevent alveolar collapse as well as decreasing elastance and increasing compliance. Caused by either smoking or an inherited deficiency of a protein called alpha 1-antitrypsin AAT.












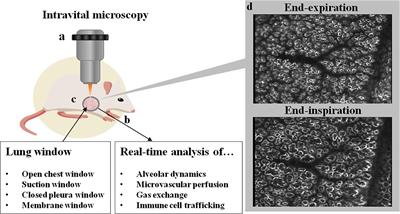


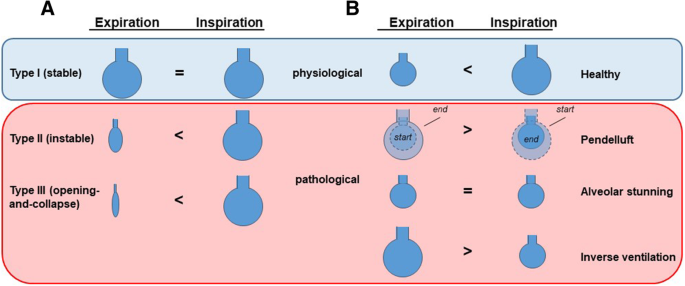

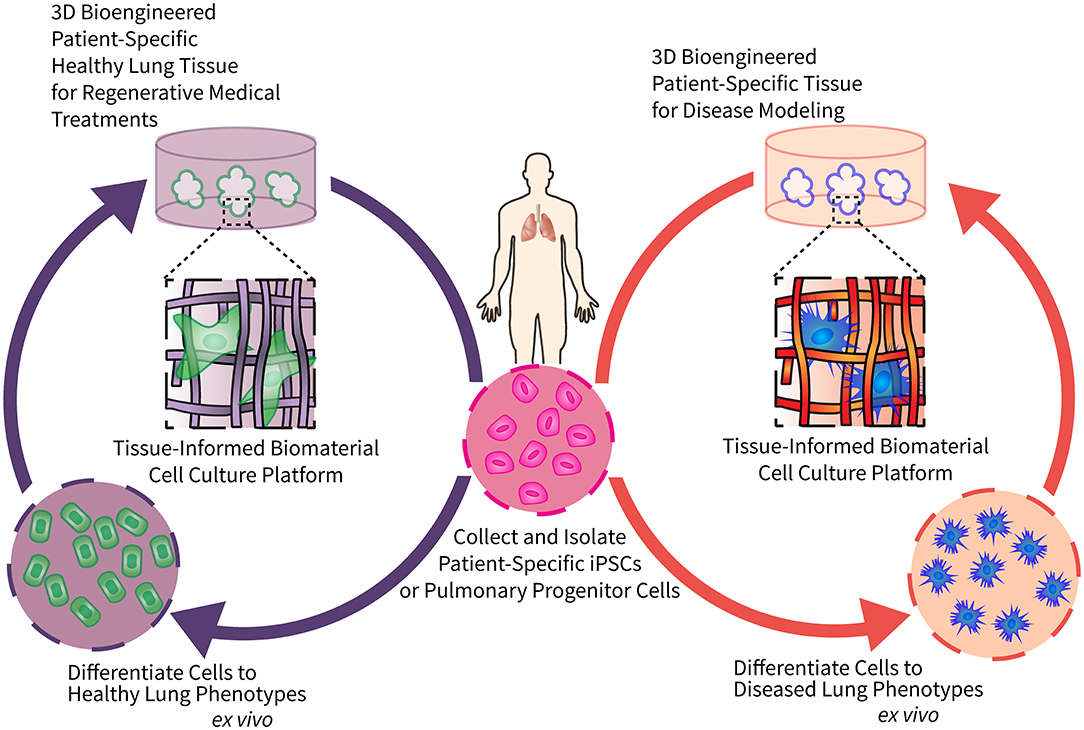
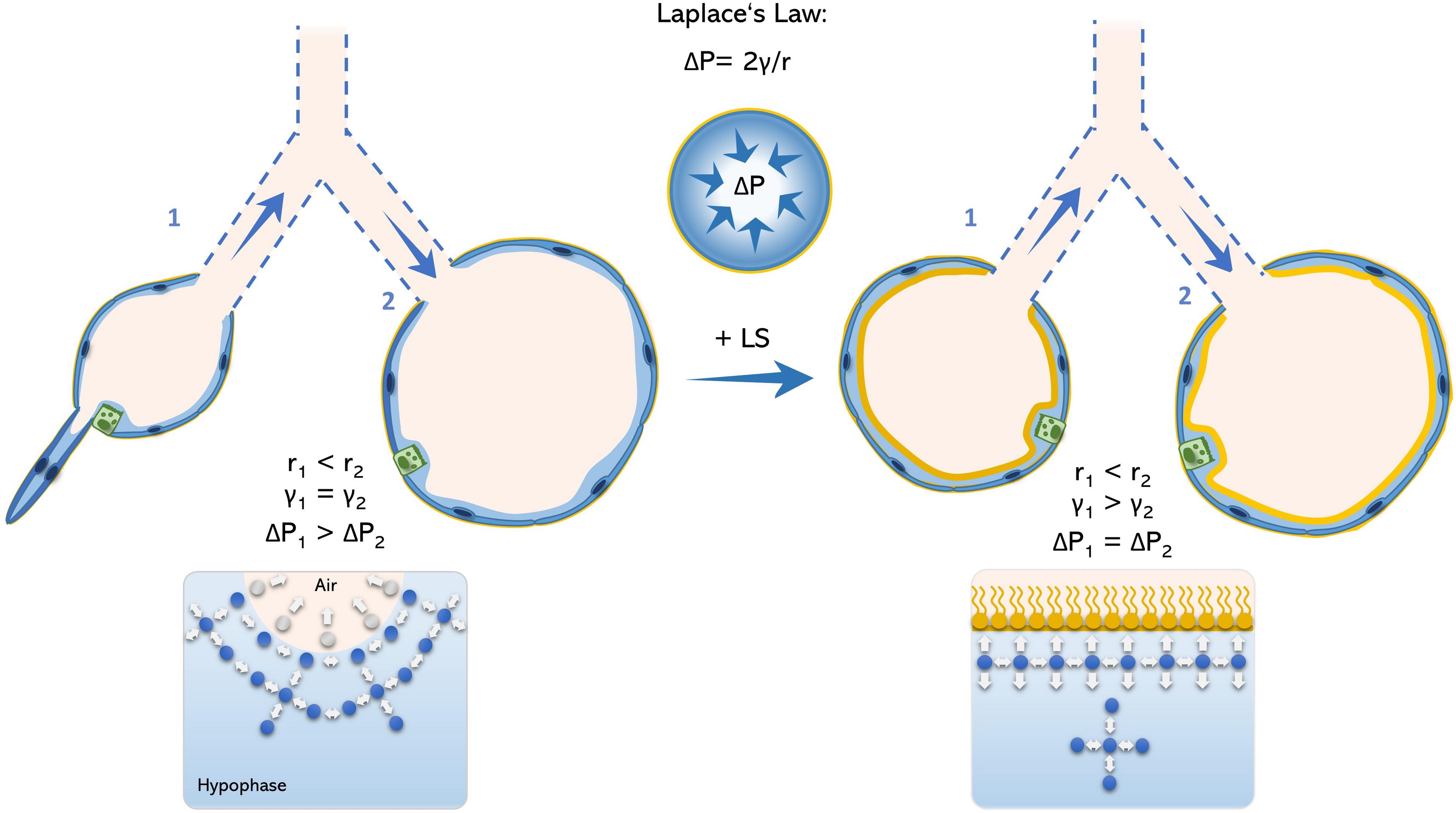







/what-are-alveoli-2249043-01-94dfddd4dfe9488b8056d586824c7c36.png)




Posting Komentar untuk "Disease Characterized By A Decrease In Alveolar Elasticity"