Wilson Disease Eye Findings
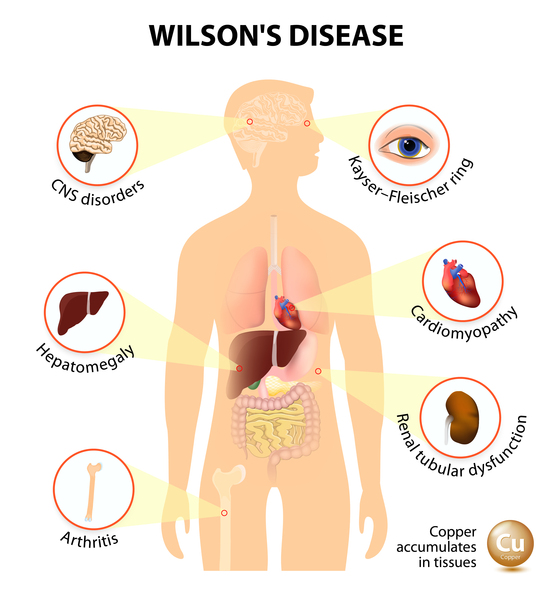
Wilson disease eye findings. Gene for Wilson disease is ATP7B on 13q which encodes a transmembrane copper transporting ATPase located on the hepatocyte canalicular membrane which assists with copper excretion into bile Most affected patients are compound heterozygotes with different mutations of ATP7B on each allele that cause defective biliary excretion of copper. Abnormalities in the putamen pons midbrain and thalamus are part of. Eye involvement in Wilson disease usually does not lead to significant impairment of vision.
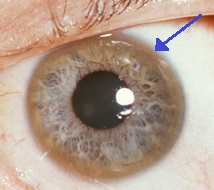
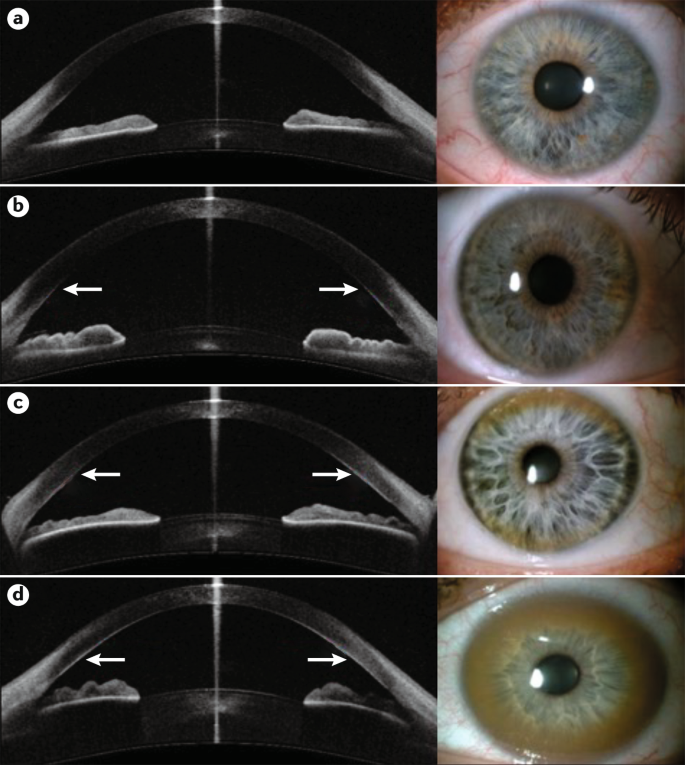
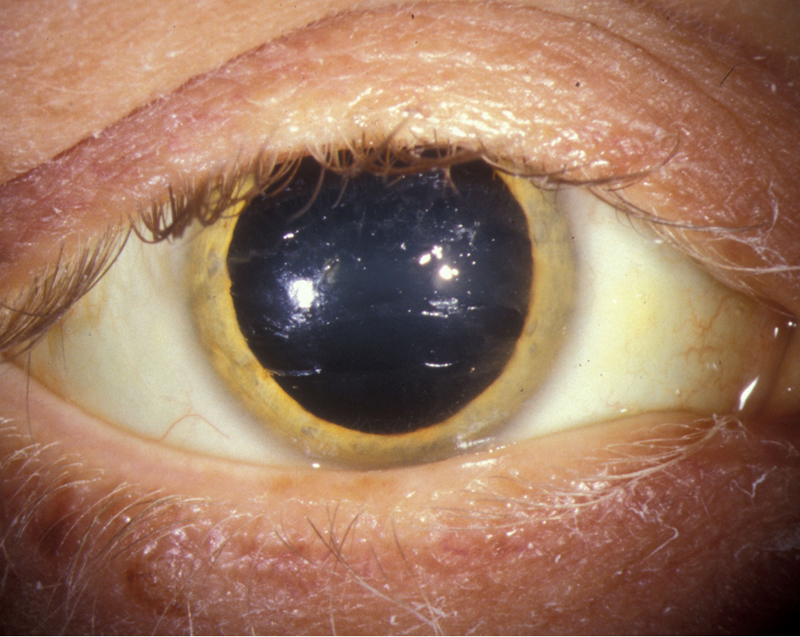
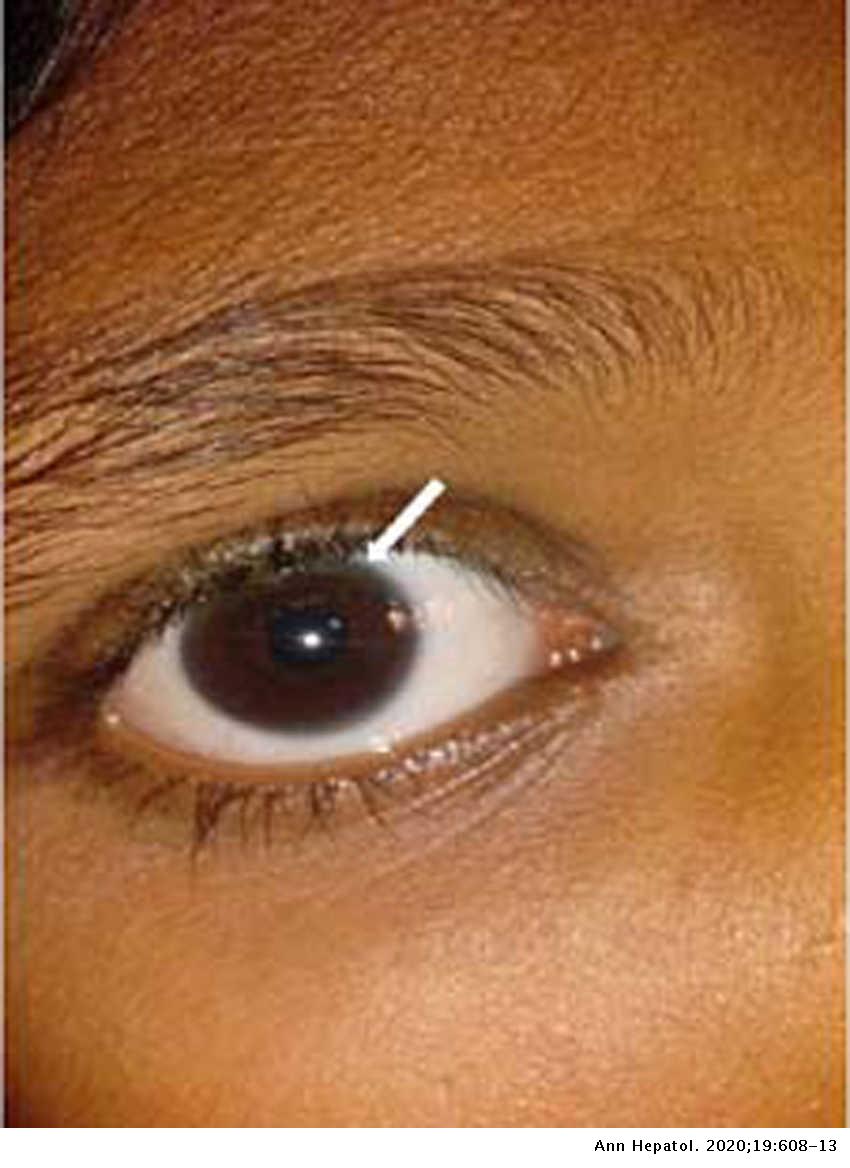
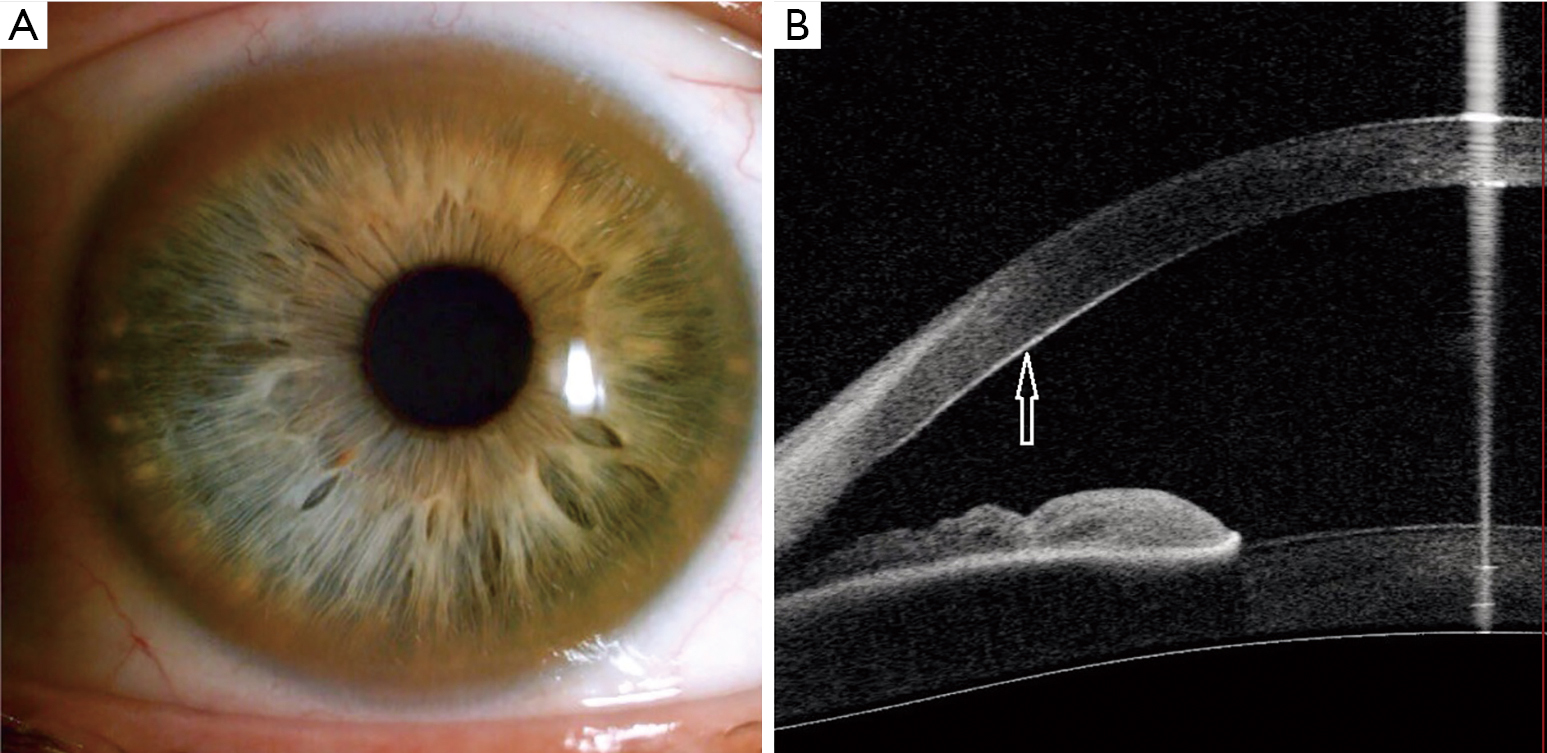
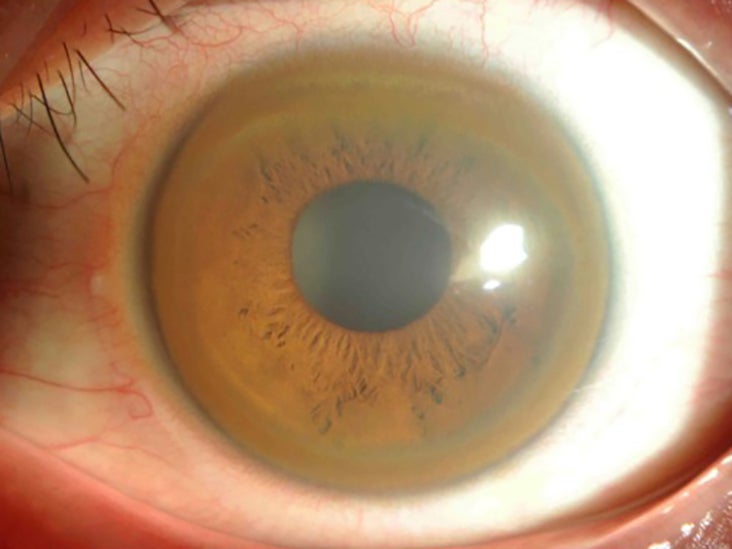
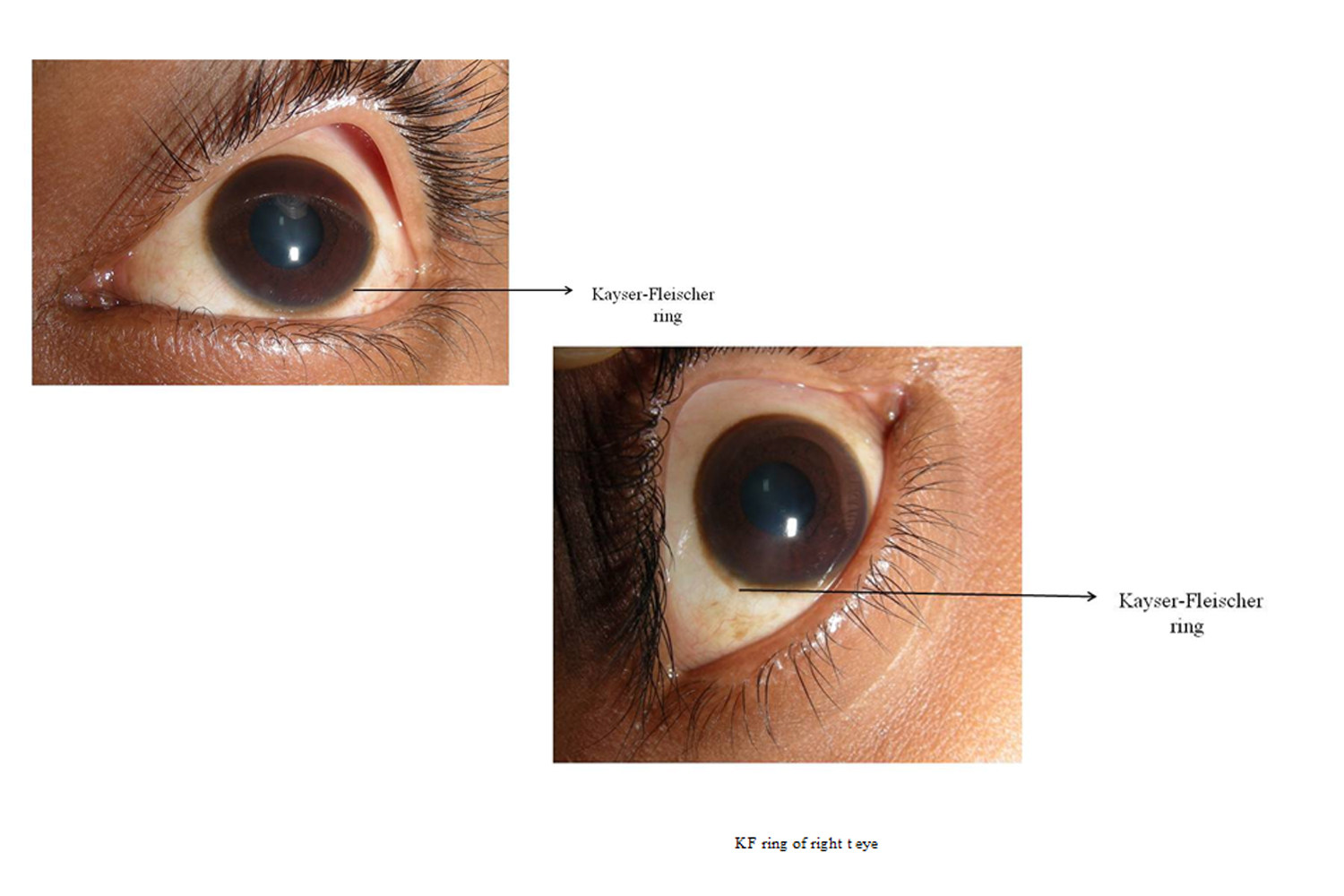
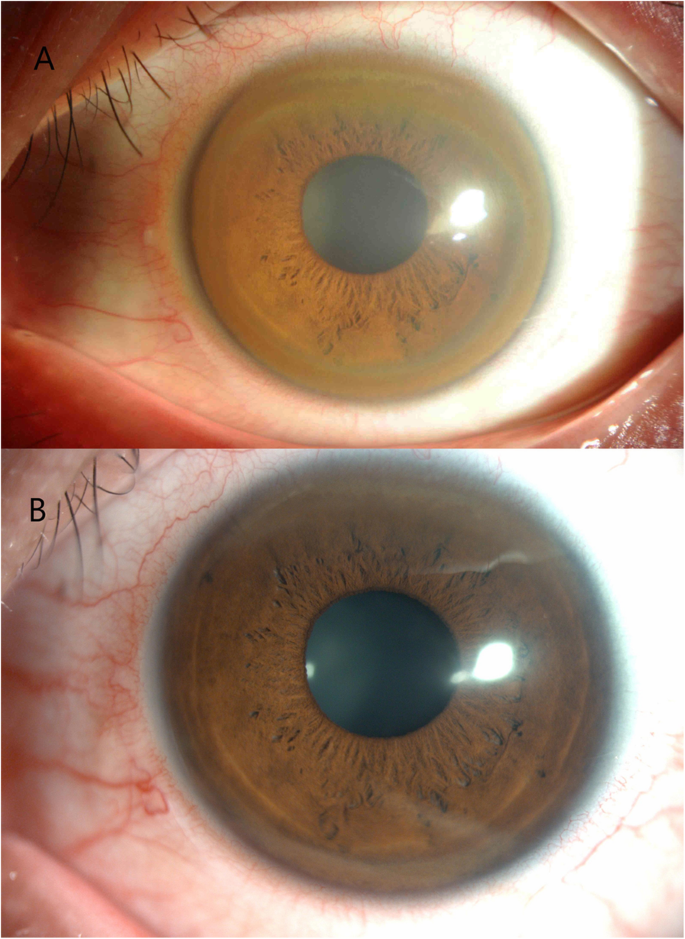
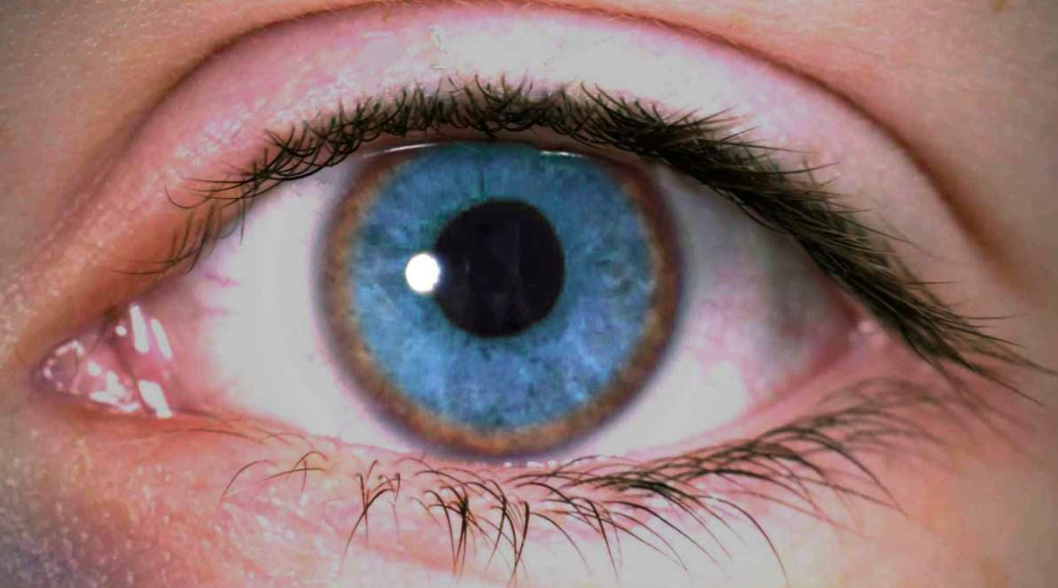
Additional ocular findings in Wilson disease include sunflower cataracts 1 saccadic pursuit movements 2 hypometric and slow saccades 3 loss of accommodation and the near response 4 and apraxia of opening the eyelid. Rusty or brown-colored ring around the iris Kayser-Fleischer rings A physical exam may show signs of. The CT scan reveals hypodense regions in.
K-F ring is almost always bilateral starts superiorly first and then inferiorly and later becomes circumferential. 6870 Special lymphoid tissue within the conjunctiva and lacrimal gland are part of the mucosa-associated lymphoid. Pathologic findings include tau containing neurofibrillary tangles in the basal ganglia midbrain cerebral cortex dentate gyrus of the cerebellum and spinal cord.
Acute hepatitis and acute liver failure Patients with Wilson disease most often children or young adults may develop acute hepatitis that is indistinguishable from acute viral hepatitis with elevated aminotransferase levels jaundice and abdominal pain. The presence of dermatological findings was not related to drug usage severity of the disease or malnutrition. The presence of Kayser-Fleischer rings typical neurologic symptoms andor low ceruloplasmin levels.
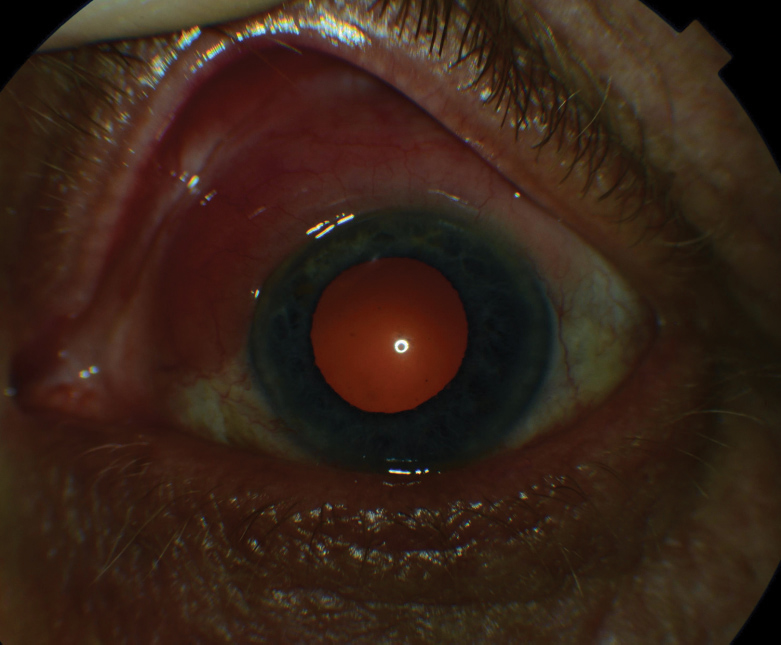
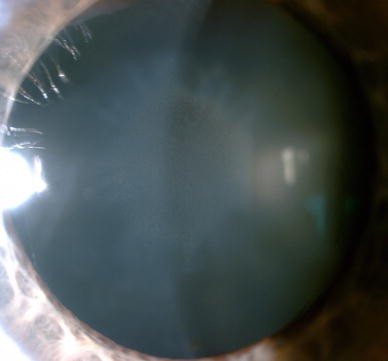
Copper deposition in the lens leads to a sunflower or sunburst cataract consisting of a greenish central disc in the anterior capsule with spoke-like radial cortical opacities. The most prevalent dermatological diagnosis of the Wilsons disease patients was xerosis 457. Computed tomography CT scan in a 15-year-old boy who presented with central nervous system findings consistent with Wilson disease.
The duration of the disease was not different in patients with or without dermatological findings. The average age of onset is 63 years with typical survival of 7 years after diagnosis. Symptoms began with the tremor 2 years prior to presentation.
Among neurologic symptoms of Wilson disease torsion spasm is associated with the midbrain and cortex and choreoathetosis is related to the caudate nucleus. Hepatic Wilson disease Children most often initially present with liver disease at an average age of 9 to 13 years.
Eye involvement in Wilson disease usually does not lead to significant impairment of vision.
The most prevalent dermatological diagnosis of the Wilsons disease patients was xerosis 457. The most prevalent dermatological diagnosis of the Wilsons disease patients was xerosis 457. Hepatic Wilson disease Children most often initially present with liver disease at an average age of 9 to 13 years. The average age of onset is 63 years with typical survival of 7 years after diagnosis. Gene for Wilson disease is ATP7B on 13q which encodes a transmembrane copper transporting ATPase located on the hepatocyte canalicular membrane which assists with copper excretion into bile Most affected patients are compound heterozygotes with different mutations of ATP7B on each allele that cause defective biliary excretion of copper. The presence of Kayser-Fleischer rings typical neurologic symptoms andor low ceruloplasmin levels. Abnormalities in the putamen pons midbrain and thalamus are part of. Damage to the central nervous system including loss of coordination loss of muscle control muscle tremors loss of thinking and IQ loss of memory and confusion delirium or dementia. The diagnosis of Wilsons disease is often based on Sternliebs criteria where a patient must have at least two of the following findings.
The presence of dermatological findings was not related to drug usage severity of the disease or malnutrition. Abnormalities in the putamen pons midbrain and thalamus are part of. The average age of onset is 63 years with typical survival of 7 years after diagnosis. 1 It results due to extracellular copper deposition in. The diagnosis of Wilsons disease is often based on Sternliebs criteria where a patient must have at least two of the following findings. Damage to the central nervous system including loss of coordination loss of muscle control muscle tremors loss of thinking and IQ loss of memory and confusion delirium or dementia. The ocular manifestations of Wilsons disease include Kayser-Fleischer ring K-F ring and sunflower cataract.
































Posting Komentar untuk "Wilson Disease Eye Findings"