Second-order System Example
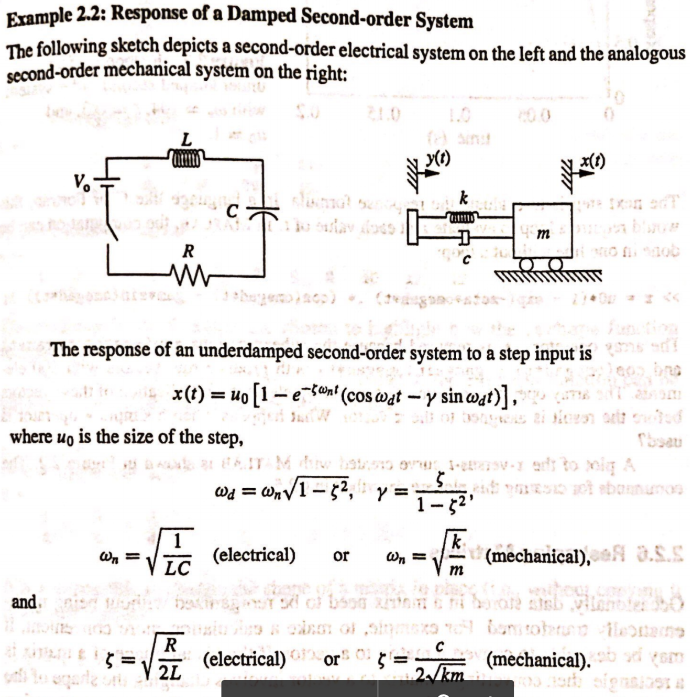
Second-order system example. Typical examples are the spring-mass-damper system and the electronic RLC circuit. Consider as an example a spring balance. The second example is a mass-spring-dashpot system.
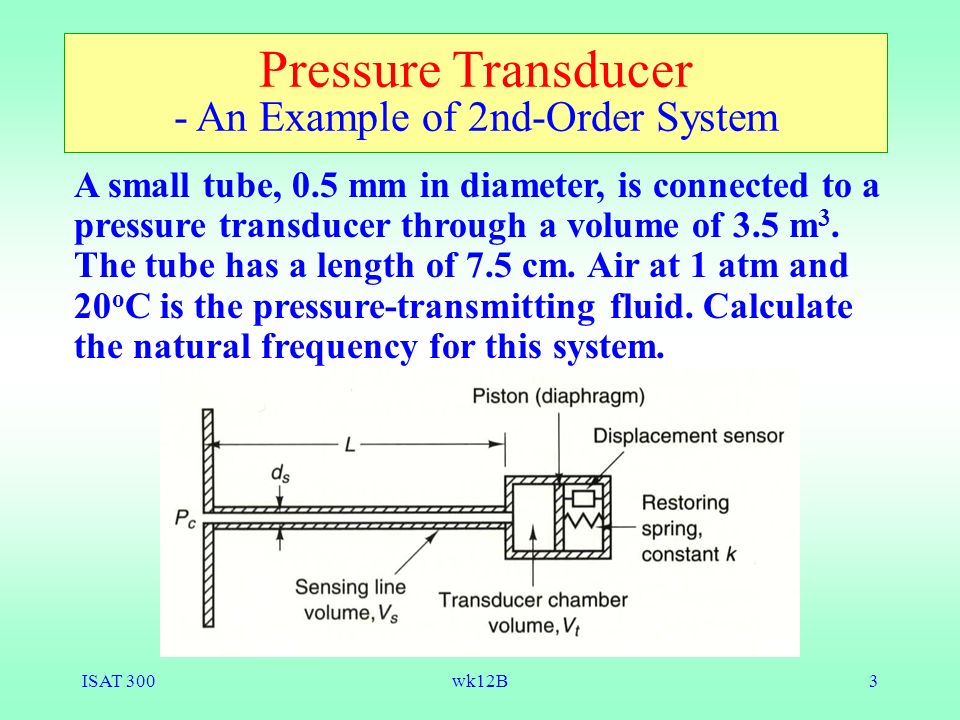
A transducer is defined as a second order system if it has two predominant energy stores. This example considers the design of a second-order system that will satisfy certain time-domain specifications. Next Topic Stability.
To better understand the dynamics of both of these systems were are going to build models using Simulink as discussed below. Determine the rise time peak time settling time and peak overshoot. This example considers the relationship between the locations of the closed-loop poles for the standard second-order system and various time-domain specifications that might be imposed on the systems closed-loop step response.
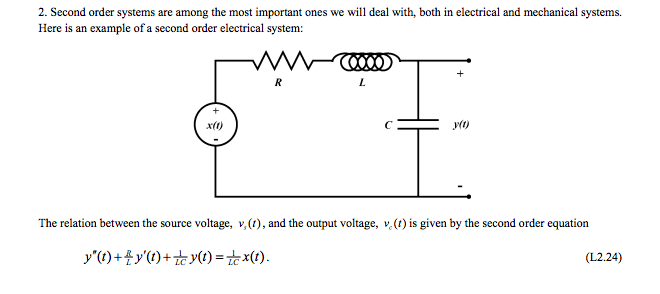
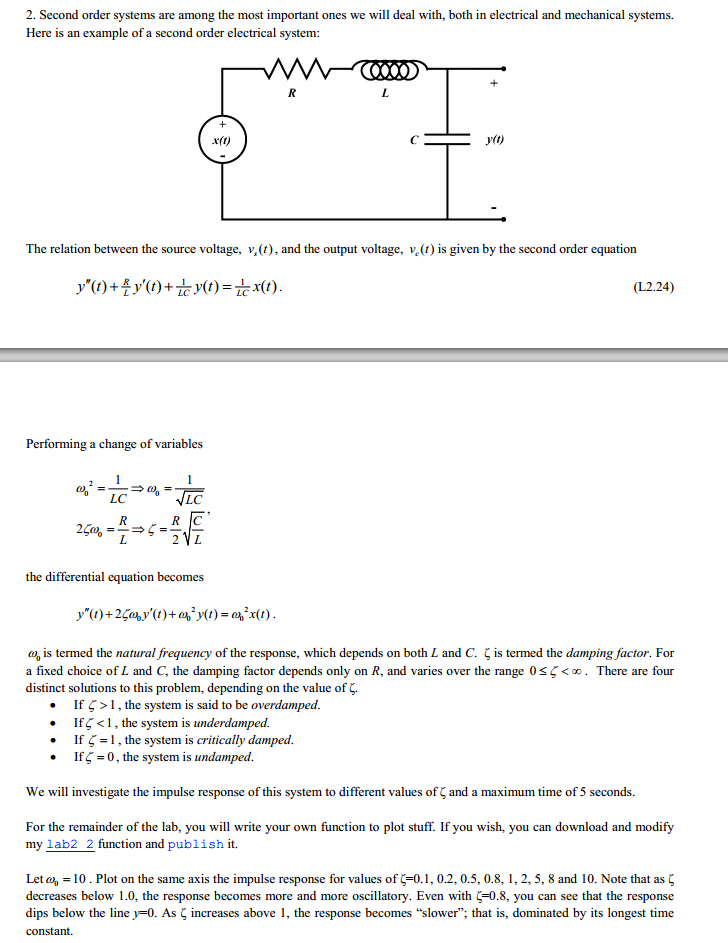
Consider the series RLC network which is an example of a second order system as shown below in Figure 3. In logic and mathematics second-order logic is an extension of first-order logic which itself is an extension of propositional logic. For example the second-order sentence P x displaystyle.
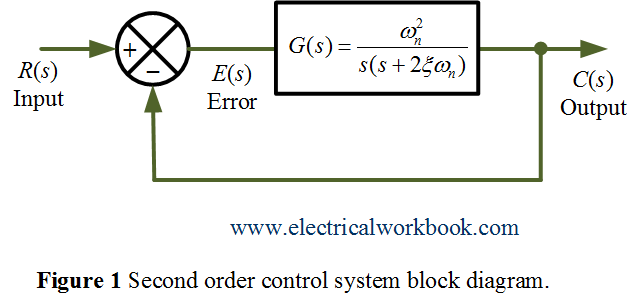
The given form and standard form are. Consider the unit step signal as an input to the second order system. To find the unit step response of the system we first multiply by 1s the Laplace transform of a unit step input.
Step Response of Second Order System. Example of a second order System using Laplace Transform Circuit Models. Describe the nature of the second-order system response via the value of the damping ratio for the systems with transfer function Second Order System 8 12 12 1.
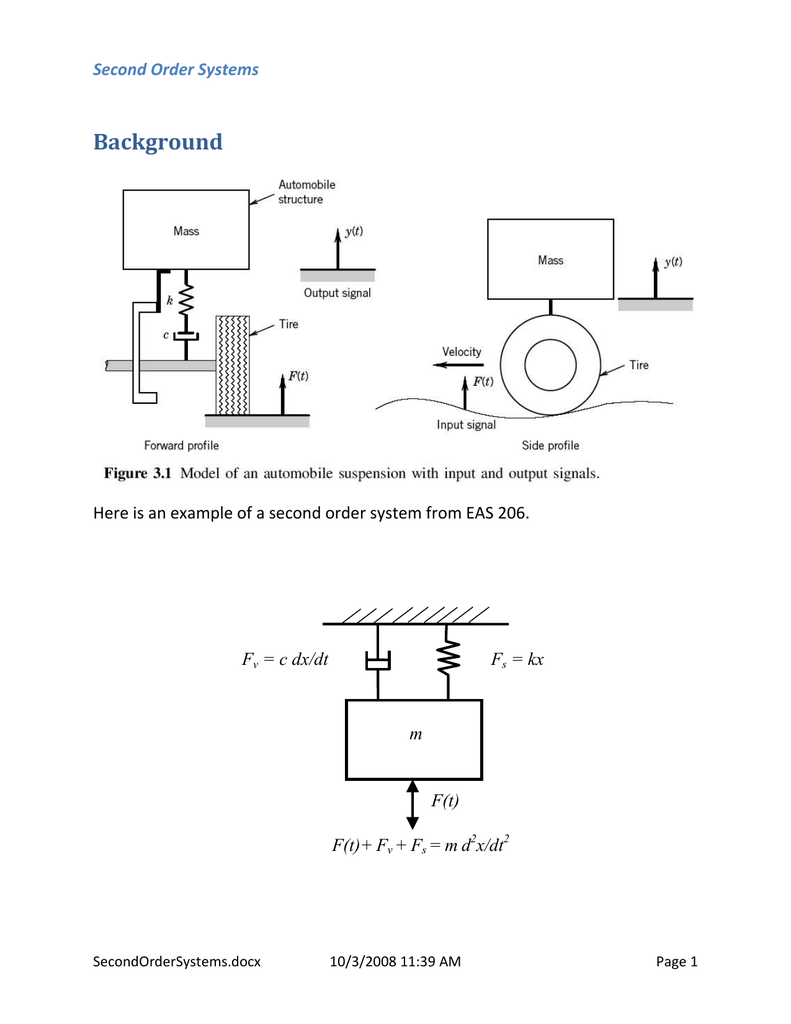
Second-order systems with potential oscillatory responses require two different and independent types of energy storage such as the inductor and the capacitor in RLC filters or a spring and an inert mass. Second Order Systems SecondOrderSystemsdocx 1032008 1139 AM Page 1 Background Here is an example of a second order system from EAS 206.
This will be done by comparing the given form for the open-loop or closed-loop transfer function with the corresponding standard form for second-order systems.
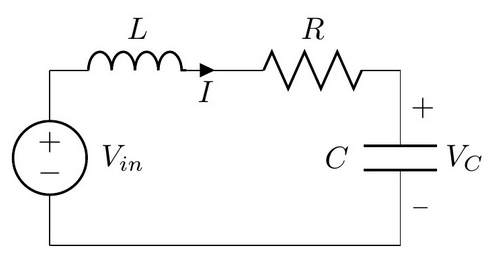
To find the unit step response of the system we first multiply by 1s the Laplace transform of a unit step input. To better understand the dynamics of both of these systems were are going to build models using Simulink as discussed below. The lateral position of the mass is denoted as x. We convert the transfer function in the following format by substituting s jω 2 1 1 ω ω j G j. Using KVL the input voltage V_is across series RLC network can be written as V_is Isleft R sL frac1sC right. RLC Step Response Example 1 Determine 𝑣𝑣 𝑜𝑜 𝑡𝑡 Input is a unit voltage step 𝑣𝑣 𝑠𝑠 𝑡𝑡 1𝑉𝑉𝑢𝑢𝑡𝑡 First apply KVL 𝑣𝑣 𝑠𝑠 𝑡𝑡𝑖𝑖𝑡𝑡𝑅𝑅𝐿𝐿 𝑑𝑑𝑖𝑖 𝑑𝑑𝑡𝑡 𝑣𝑣 𝑜𝑜 𝑡𝑡 0. Is modeled using a first-order differential equation. 122 Mechanical second-order system The second-order system which we will study in this section is shown in Figure 119. 2 s s G s 8 16 16 2.
Second-Order System Example 4. Is modeled using a first-order differential equation. To find the unit step response of the system we first multiply by 1s the Laplace transform of a unit step input. Second-order logic in addition also quantifies over relations. Second-Order System Example 3. 1 We call 2 1 ω the break point. Additionally the mass of the system the mechanism as well as the mass we are measuring can store energy kinetic energy.
























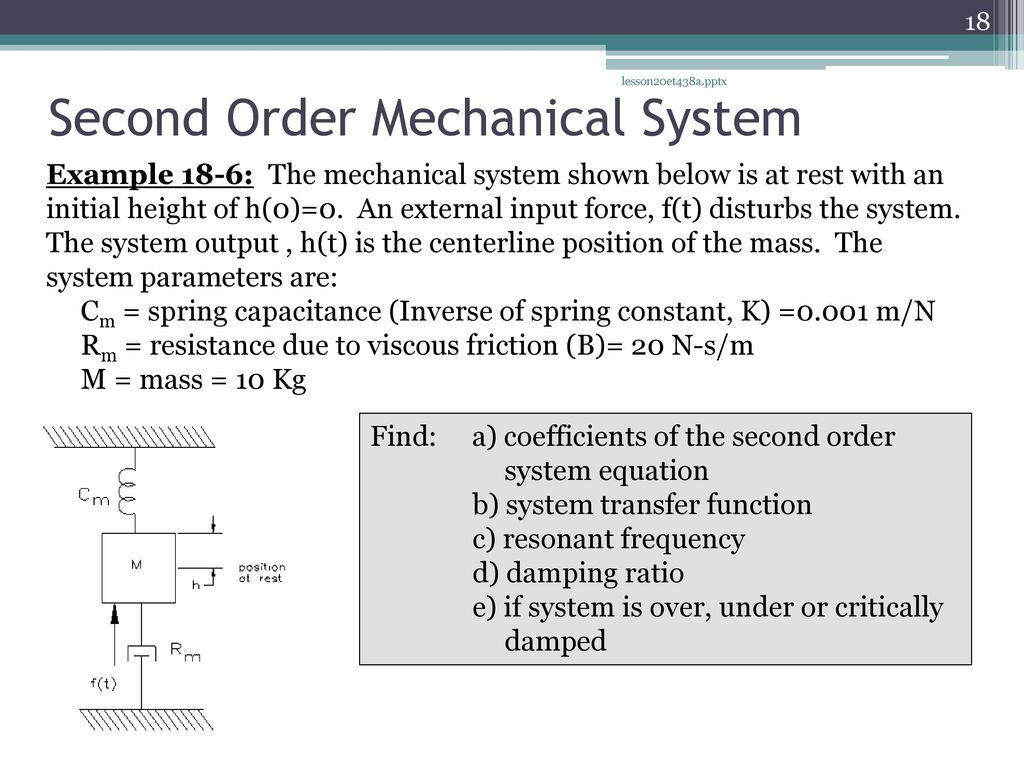

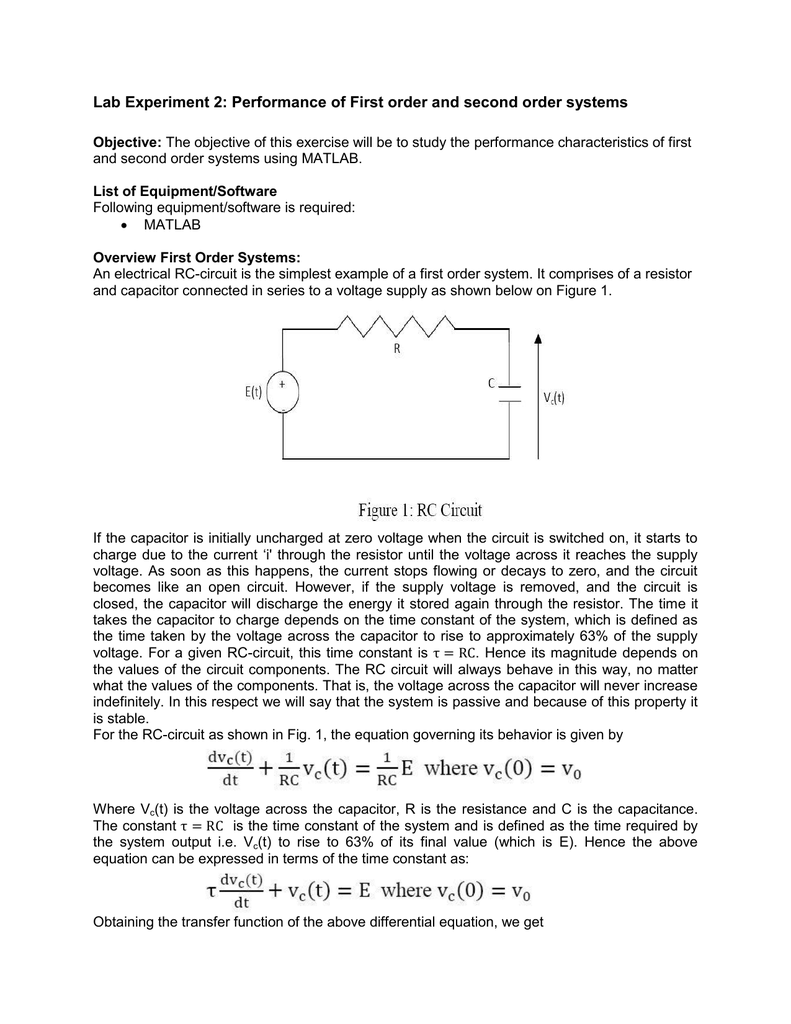


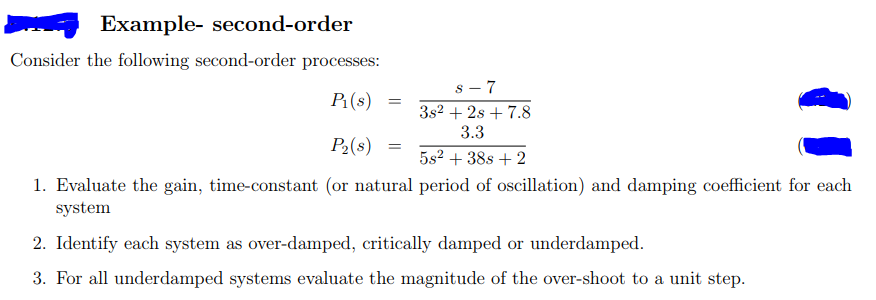
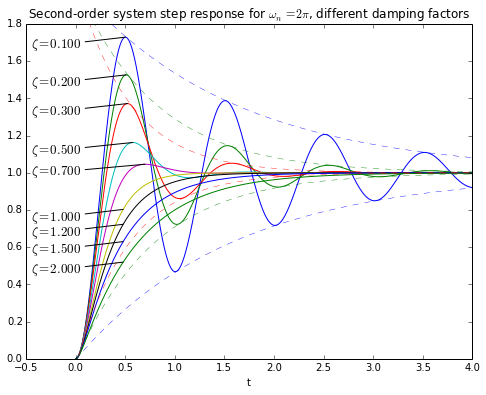



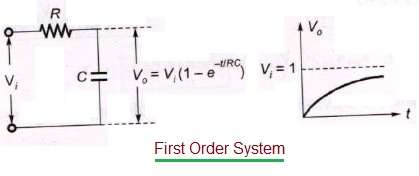
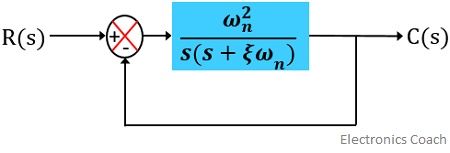
Posting Komentar untuk "Second-order System Example"